Breech Presentation: What It Is and How It Can Affect Your Baby's Delivery
As you get close to your due date, your baby might sense she’s approaching her grand entrance and move into a head-down position in your uterus, ready to be born. However, in some cases, she might choose another position instead, such as bottom or feet down. When this happens, it’s called a breech presentation. Read on to learn how your healthcare provider checks the position of your baby, what delivery options you may have if your baby is breech, and what can cause a breech presentation.
What Is Breech?
During your pregnancy, your baby has likely taken every opportunity to let you know she means business by kicking up a storm and doing countless somersaults. It's natural for your baby to move and shift positions within the uterus. Then, usually between 32 and 36 weeks of pregnancy, your baby will likely get into a head-down position in preparation for being born. There is a small chance—just 3 to 4 percent—that your baby may not move into this head-down position by the time your pregnancy is full term. This is called a breech presentation. The chance of a breech presentation is higher if your pregnancy is not yet full term or if you go into preterm labor.
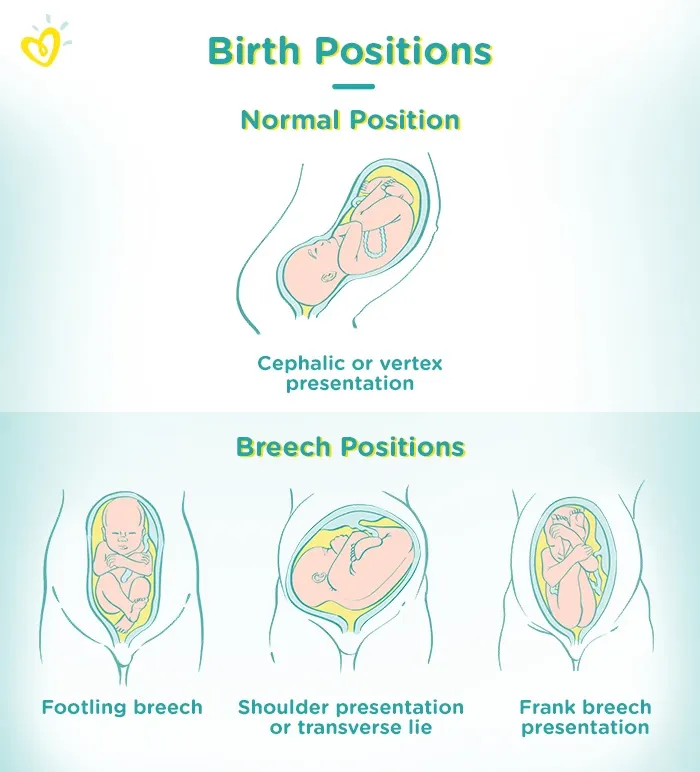
Types of Birth Positions
There are many different types of positions, including a number of breech presentations, which your baby may take on before birth:
Cephalic or vertex presentation (occiput). Your baby is in the normal position for delivery. Her head is down and she’s facing toward your back.
Footling breech. One or both of your baby's feet are pointed downward.
Shoulder presentation or transverse lie. This is a form of breech in which your baby is positioned horizontally in the uterus. Few babies remain this way at the time of delivery.
Frank breech presentation. Your baby's bottom is positioned downward. This is the most common type of breech presentation.
Complete breech presentation. Your baby's feet are positioned downward with her hips and knees flexed, almost cross-legged.
Incomplete breech presentation. Your baby's feet are positioned downward with only one hip or one knee flexed.
Cephalic or vertex presentation (occiput posterior). In some cases, your baby may be in a downward position but with her face toward your front. If this happens in early labour, your baby may naturally turn to face your back on her own, or, later in labour, your provider may decide to manually assist the baby in getting into this position. If this doesn't work, your baby can still be delivered vaginally, but delivery may be prolonged and more painful.
Causes
The causes of your baby being in breech position aren't always clear, but it can be more common if any of the following apply to you:
You are pregnant with twins (read on to learn more about twin breech)
The uterus has more or less amniotic fluid than usual
The uterus has an abnormal shape or has abnormal growths, such as fibroids
You have a condition called placenta previa, which is when the placenta covers the cervix.
Your healthcare provider likely already knows whether any of these factors affect your situation, but you might want to mention it just to be sure.
Diagnosis of a Breech Presentation
At one of your prenatal visits in the lead up to your due date, your provider will check that everything is progressing as planned, and will examine your abdomen to try to find out whether your baby is in the correct head-down position. If your provider thinks there may be a breech presentation, she or he may recommend an ultrasound exam to confirm it.
Can a Breech Baby Be Turned?
If your baby is breech, your provider may consider turning your baby so that a vaginal delivery can proceed. Alternatively, your provider may recommend that a cesarean delivery is the safer option. Keep in mind, your baby's position might change at some point before delivery day, so your provider may recommend waiting and seeing. If you are 37 weeks pregnant or more, your provider may recommend turning your baby through a process called external cephalic version or ECV. ECV involves your provider placing hands on your abdomen and applying firm pressure in order to turn the baby. This procedure will most likely be done near a delivery room. Your provider may offer an epidural block to help with any pain this procedure causes. An ECV is about 50 percent effective and there is a small risk of complications. You and your baby will be monitored closely before, during, and after the procedure to ensure that both of you are doing well. If the ECV procedure is successful, your baby can be delivered vaginally, if there’s no other impediment.
Delivery Options for a Breech Baby
If your baby is in a breech position, the risks associated with a vaginal delivery are much higher than with a cesarean section. Risks include the umbilical cord cutting off his blood supply or his head or shoulders becoming stuck. That’s why, in some cases, your provider may recommend a cesarean delivery. It could be that your provider’s level of experience in delivering breech babies might also inform the discussion you have with your provider about what’s right for your situation. Ultimately, your provider will recommend the best course of action for you and your baby based on your personal situation.
Twins and Breech Presentation
It’s possible for twins to be delivered vaginally if the first baby—the lower-positioned twin—is correctly positioned with the head facing down. Of course, that’s if the twin pregnancy is otherwise progressing well and there are no complications. If the second twin is in a breech position, the provider may do an ECV procedure to get this baby in the correct head-down position for a vaginal delivery, too. If the first twin baby (the one lower down) is in a breech position, the provider may recommend a cesarean section. Triplets or more will most likely require a cesarean section.
Although you might feel like the added stress of a breech baby is the last thing you need as you approach your due date, remember that your healthcare provider has seen this situation before and will know what to do to ensure your baby is delivered safely. Next thing you know, you'll be bringing your brand-new baby home, stocking up on diapers, waking up for late-night feedings, and reveling in your baby's growth. To start earning rewards for all those diapers you’re stocking up on, download the Pampers Rewards app.
How We Wrote this Article
The information in this article is based on the expert advice found in trusted medical and government sources, such as the American Academy of Pediatrics and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. You can find a full list of sources used for this article below. The content on this page should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult medical professionals for full diagnosis and treatment.
Join Pampers Club and get: